Immulina +D3
GENERAL REMARKS
Immulina + D3 it is further development of Immulina plus. This new product provides the same active compounds as Immulina plus and additionally provides 4.000 international units of Vitamin D3 (100 µg) and 120 µg selenium amount for 2 capsules ia. recommended daily amount of product. Immulina + D3 — is available in 30 capsules packages only, for the time being.
Immulina + D3 is a complex preparation. One may say it has three groups of active ingredients that we are trying to characterize hereinafter.
Active Ingredients
First Group of Ingredients
There are two macromolecular compounds in this grup. It is lipopolysaccharide complex LCEPEEN form spirulina extract and β-1,3/1,6 D-glucan from backer's yeast extract. These two ingredients only are immunomodulators and show real immunomodulatory activity. Immunomodulators are active substances applied in immunotherapy. Immunomodulation is a modulation - regulatory adjustment - of immune system. Immunomodulation as part of immunotherapy, in which immune responses are induced, amplified, attenuated, or prevented according to therapeutic goals.
IMMUNOACTIVE SPIRULINA EXTRACT

Spirulina Extract provides a macromolecular lipopolysaccharide compound coded by manufacturer the Danish Company Nordic ImmoTech as LCEPEEN. This product was invented by team of scientists from National Center for Natural Products Research at University of Mississippi under leadership of Dr David S. Pasco, pharmacy professor. Spirulina extract was marketed under Immulina trade name. LCEPEEN complex exhibits outstanding immunomodulatory properties superior than other available immuno-supplements (see figures and tables below).
Swallowed LCEPEEN complex form Immulina is phagocyted by macrophages and dendritic cells (phages of digestive tract) – so called antigen presenting cells. After LCEPEEN digestion APC become activated.
LCEPEEN the most potent immune booster in relationship to the macrophages and monocytes activation click picture to magnify ReishiMax - polysaccharide from fungi Ganoderma Lucidum |
Immunostimulating Potency of Different Plants Expressed as amount of plant needed to produce the same stimulating effect in relationship to activation of macrophages/monocytes click picture to magnify |
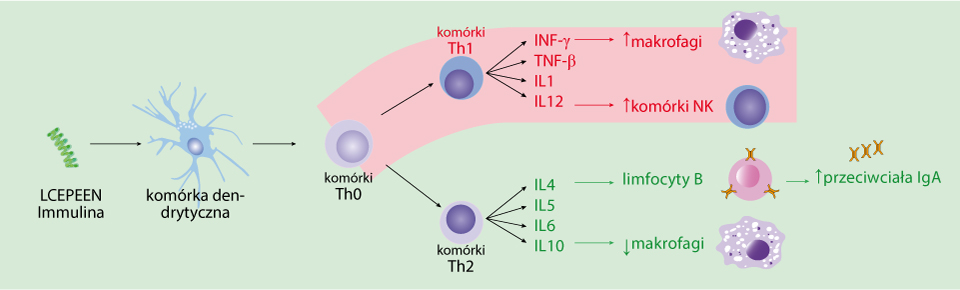
* Interleukines – group of several dozens proteins so called cytokines taking part in immune and haematopoetic processes. Interleukine 12 (IL-12) initializes T lymphocytes differentiation in direction of Th1 type cells, activates NK cells, monocytes and macrophages, especially stimulates these cells to produce interferon-γ.
IL-1β is secreted in response to various antigens of viral, bacterial and fungal origin. It has an activating effect on leukocytes and many other cells not directly related to the immune system, because it is also involved in tissue remodeling, synthesis of acute phase proteins, causes drowsiness and is a pyrogen.
Immulina containing active LECPEEN complex has been compared to crude lipopolysaccharide (LPS) that are component of cell wall of Escherichia coli. Immulina 8-times more effective affects immunity more effectively in comparison to Escherichia coli lipopolysaccharides and 20 times than aloe vera and 25 times than spirulina from which it is derived. This is because Immulina acts on the immune system through TRL-2 receptors*, which have much higher density (more than 2.5 times) on the surface of antigen-presenting cells (dendritic cells) than TLR-4 receptors, through which most substances act affecting immunity. Immulina affects immunity up to 40 times more effectively compared to traditional preparations such as echinacea and β-glucan. Preparations containing reishi and American ginseng extracts show practically only trace effects in comparison to LCEPEEN in Immulina.
Comparison of the potential of various natural activators of the NF-κB factor
Table 1.
| Compound Name* | NF-κB Activation in THP1 monocytes (EC50 Value**) |
Natural Source |
|---|---|---|
| LCEPEEN Immulina |
||
| Crude LPS | ||
| Aleoride | ||
| Zymosan A | ||
| Arabinogalaktan | ||
| Polisacharyd K | ||
| MGN 3 | ||
| Acemannan | ||
| Lentinan | ||
| Schizophylan |
* Compound name – all compounds are high molecular weight polysaccharides or lipo-polysaccharides.
** The EC50 value represents the amount (in nanograms) of each of the tested formulations needed to achieve 50% of the maximum activation of nuclear factor NF-κB obtained with LPS.
Crude lipopolysaccharides (LPS) have so far been considered the strongest activator of the nuclear factor NF-κB and the effects of the tested products were related to them. In the tests carried out, it was found that Immulina is more active than lipo-polysaccharides (LPS).
THP monocytes - own line of monocytes developed by the laboratory.
The innate immune response is an evolutionarily older form of immunity than the acquired response. It is fast and quite well targeted, it does not initiate the destruction of its own tissues, but it does not leave a permanent immunological memory. The LCEPEEN complex (from spirulina extract) binds to the appropriate receptors of antigen-presenting cells (patterns recognizing receptors - PRR), which usually leads to the activation of the nuclear transcription factor NF-κB and the increase in the expression of genes encoding pro-inflammatory cytokines and the rapid induction of an immune response.
Effect of a diet containing spirulina extract on the concentration of IgA and INF-γ

In laboratory studies, a diet containing LCEPEEN (lipopolysaccharide complex) from spirulina extract has been shown to increase the concentration of immunoglobulin antibodies of the IgA class and interferon gamma (INF-γ) after a few days. Immunoglobulins* are produced by activated B lymphocytes. mucosal immune response immunoglobulins. Thanks to them, the body protects itself against the penetration of microorganisms (bacteria, viruses) through the mucous membranes.
Interferon gamma belongs to a group of 10 interferons - proteins produced and released by body cells in response to the presence of pathogens (e.g. viruses, bacteria, parasites as well as cancer cells) inside the body. Interferons ensure communication between body cells to fight pathogens by triggering defense mechanisms of the immune system. IFN-γ has antiviral properties and plays an essential role as a mediator of the body's immune response, e.g. to infection and cancer.
* Immunoglobulins - immune proteins are divided into 5 main classes – G, A, M, E and D – IgG, IgA, IgM, IgE and IgD. Immunoglobulins play a major role in the humoral immune response. Immunoglobulins are produced by active forms of B lymphocytes - plasma cells in response to an antigen, i.e. a pathogen that stimulates the immune system.
IMMUNOACTIVE BETA-GLUCAN
β-glucans are high-molecular polysaccharides, i.e. polysaccharides commonly found in the plant world. They are one of the components of the cell wall of many plants, especially cereals and fungi. Depending on their origin, β-glucans have different structures and different properties. In general, they can be divided into two main groups that have been used due to their significant health properties:
(1) Soluble β-glucans derived mainly from cereals (oats, barley, rye, etc.) and
(2) Insoluble β-glucans derived mainly from mushrooms (yeast, shiitake mushroom, oyster mushroom, reishi mushroom, split gill mushroom, etc.)
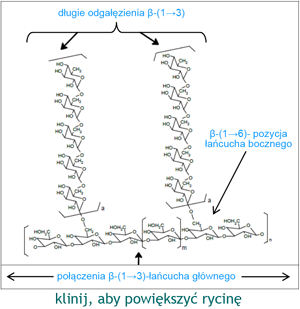
The first group, showing in its structure short chains with β-bonds in positions (1→3)-(1→4), is soluble in water. This group of β-glucans has outstanding properties influencing the carbohydrate-lipid economy in humans. Their consumption lowers/normalizes lipid (cholesterol) and blood sugar levels.
The second group, showing in its structure long chains with β-bonds in positions (1→3)-(1→6), is insoluble in water. They have immuno-modulating properties. Their consumption supports the natural, non-specific immunity of the body.
These macromolecular β-1,3/1,6-D glucans are a common ingredient in various immuno-modulating preparations used in various clinical situations. Particularly large amounts of β-1,3/1,6-D glucans are found in the cell wall of baker's yeast (Saccharomyces cerevisiae). It is the most immunologically active fraction from the whole group of β-glucans. It is composed of D-glucose molecules linked at the 1,3-position and with D-glucose side chains linked at the 1,6-position. The figure opposite shows the structure of the insoluble β-1,3/1,6-D glucan molecule with a long chain, derived from baker's yeast.
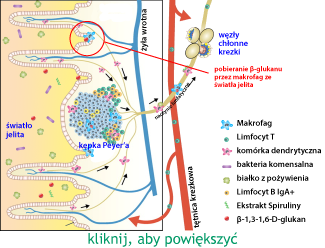
After swallowing, β-glucan particles are phagocytized by macrophages and dendritic cells, i.e. antigen-presenting cells, and through them by the lymphatic tissue of the digestive tract, so called GALT, they stimulate the entire immune system. It was believed that β-glucan participates in the activation of cellular immunity only in this way, and for many years glucan was treated as a non-specific stimulator of macrophages. This is a very important process for the body, because macrophages form the first line of defense and without their optimal activity, the body cannot effectively defend itself. The figure below shows the uptake of β-glucan from the gastrointestinal tract and its effects on the immune system.
It used to be thought that β-glucan could only modulate the immune system when used parenterally, due to the lower systemic bioavailability of oral formulations. However, many studies, both in vitro and in vivo, have revealed that orally administered β-glucan also exerts such an effect. The interaction was discovered through different receptors, explaining the possible modes of action. The effects depend mainly on the origin and structure of β-glucans. At the same time, many clinical trials of insoluble yeast β-glucans administered orally were conducted. The obtained results confirmed the results of previous in vivo studies. Taken together, the results of all the studies clearly indicate that oral administration of yeast β-glucans is safe and has an immune-enhancing effect.
Due to the low systemic availability of oral preparations, it has been thought that only parenterally applied beta-glucans can modulate the immune system. However, several in vivo and in vitro investigations have revealed that orally applied beta-glucans also exert such effects. Various receptor interactions, explaining possible mode ofactions, have been detected. The effects mainly depend on the source and structure of the beta-glucans. In the meantime, several human clinical trials with dietary insoluble yeast beta-glucans have been performed. The results confirm the previous findings ofin vivo studies. The results of all studies taken together clearly indicate that oralintake of insoluble yeast beta-glucans is safe and has an immune strengthening effect.
Review of clinical data by: Stier H, Ebbeskotte V, et al → Immune-modulatory effects of dietary Yeast β-1,3/1,6-D-glucan Nutrition Journal;2014,13:38 (pdf 12 stron).
Research review article by: Kim HS, Hong JT, et al → Stimulatory Effect of β-glucans on Immune Cells Immune Netw.;2011 Aug;11(4):191-195